By Allan Armstrong and Doug Arnold
The power grid is experiencing rapid change. Population growth and highly-consumptive industries – datacenters, IC fabs, mining & metal smelting – are driving capacity expansion. Green energy is rushing in to help, but solar and wind are distributed through the network and less predictable. Unlike thermal power plants, the wind blows when the wind blows and the sun shines when the sun shines. This all means that power flows are changing rapidly, which challenges the stability of the grid.
To keep the grid stable, power operators must measure power flows at an increasing number of points within the grid, collect this information to estimate state, and take actions to stabilize the grid.
So, phase measurement units (PMU) are being installed throughout power grids. A PMU is an A-D converter that monitors voltage or current and reports it across the network to a central control system (see Figure 1). Because the grid must compare time-aligned measurements hundreds and thousands of km apart the PMUs require time synchronization. Timestamped phase measurements of voltages or currents are referred to as synchrophasors. Sometimes PMUs themselves are referred to as synchrophasors but it is more precise to refer to the measurements that PMUs produce as synchrophasors.
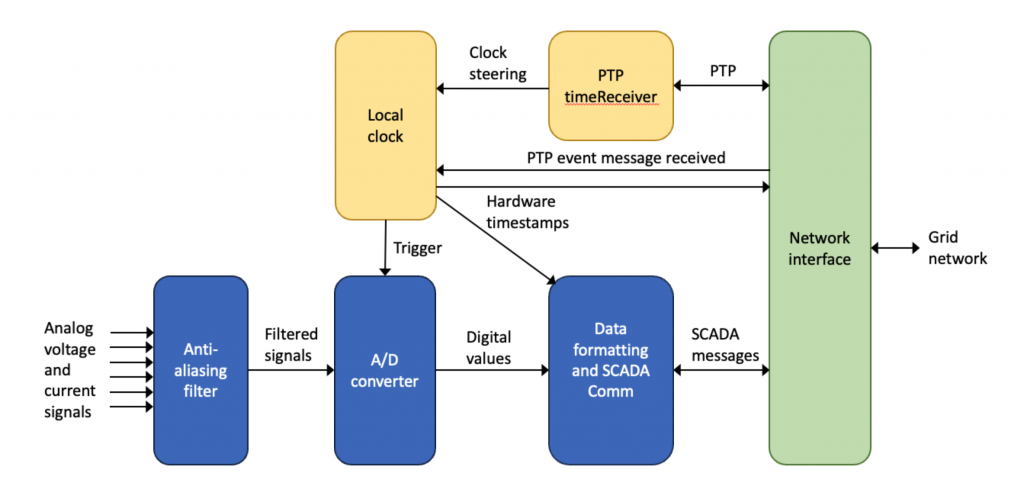
The IEEE C37.118 standard recommends that Synchrophasors have time accuracies of 1 microsecond to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). This accuracy guarantees that the current and voltage phase measurements made at different locations can be compared with negligible error contributed by the timestamp accuracy.
Now that the PMUs are synchronized and producing accurate synchrophasor measurements what do we do with all that data? Synchrophasor experts help each other answer that question, as well as developing best practices for PMU deployment at NASPI, the North American SynchroPhasor Initiative. NASPI is user group for the synchrophasor community.
Grid stability is a really challenging problem. It is a discrete time system with large delays across the network, modeling the network elements is difficult, green energy is placing additional demands on the network, and the network spans legal and organizational boundaries. For these reasons, PMUs are an essential technology for the safe and reliable operation of the grid.
For more on the needs of timing in power grids see this previous post.
If you have any questions about packet timing, don’t hesitate to send me an email at doug.arnold@meinberg-usa.com or visit our website at www.meinbergglobal.com.
If you enjoyed this post, or have any questions left, feel free to leave a comment or question below.